Pro Read: As a leak indicates that Autel Robotics may be the first to offer a 6/8K camera on a drone, UAS expert and industry leader Douglas Spotted Eagle dives in to what the advantages of 8k may be – and if the drone industry is ready to take advantage of them.
Guest post by Douglas Spotted Eagle, Founder and Director of Educational Programming at Sundance Media Group.
In 2004, Sony released the world’s first low-cost HD camera, known as the HVR-Z1U. The camera featured a standard 1/3” imager, squeezing 1440×1080 pixels (anamorphic/non-square) pixels on to the sensor. This was also the world’s first pro-sumer camera using the MPEG2 compression scheme, with a color sample of 4:2:0, and using a GOP method of frame progression, this new technology set the stage for much higher resolutions and eventually, greater frame rates.
It’s “father,” was the CineAlta HDWF900, which offered three 2/3” CCDs, which was the industry standard for filmmaking for several years, capturing big hits such as the “Star Wars Prequel Trilogy”, “Once Upon a Time in Mexico”, “Real Steel”, “Tomorrowland”, “Avatar”, “Spykids” (1 & 2), and so many others. The newer HDV format spawned from similar technology found in the HDWF900, and set the stage for extremely high end camera tech to trickle down into the pro-sumer space.
Overtime, camera engineers identified methods of co-siting more pixels on small imagers, binning pixels, or using other techniques to increase the capture resolution on small surfaces. Compression engineers have developed new compression schemes which brought forward AVC (h.263), MP4(h.264), and now HEVC/High Efficiency Video Codec(h.265), and still others soon to be revealed.
Which brings us to the present.
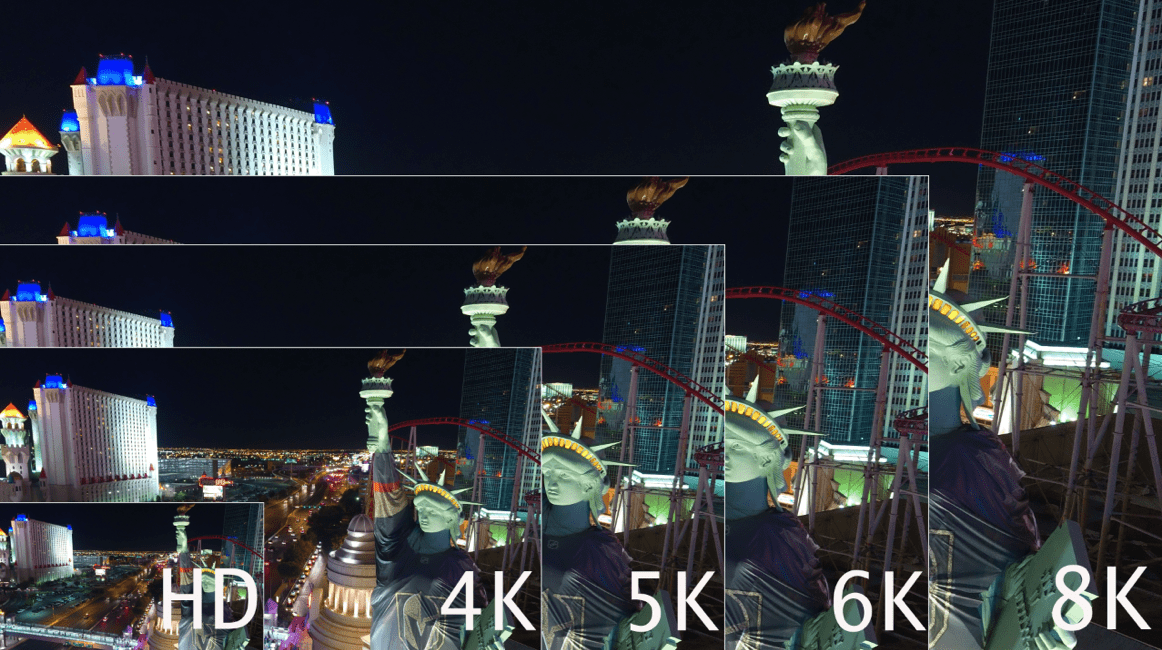
We have to roughly quadruplemegapixels to doubleresolution, so the jump from SD to HD makes sense, while the jump from HD to UHD/4K makes even more sense. Following that theme, jumping to 6K makes sense, while jumping to 8K is perfect theory, and nears the maximum of the human eye’s ability to resolve information.
At NAB 2018, Sony and Blackmagic Design both revealed 8K cameras and in that time frame others have followed suit.
During CommUAV and InterDrone, several folks asked for my opinion on 6 and 8K resolutions. Nearly all were shocked as I expressed enthusiasm for the format.
– “It’s impossible to edit.”
– “The files are huge.”
– “No computer can manage it.”
– “There is no where to show 8K footage.”
– “Human eyes can’t resolve that resolution unless sitting very far away from the screen.”
– “Data cards aren’t fast enough.”
And….so on.
These are all the same comments heard as we predicted the tempo of the camera industry transitioning from SD to HD, and from HD to 4K. In other words, we’ve been here before.
 Video cameras are acquisition devices. For the same reasons major motion pictures are acquired at the highest possible resolutions, and for the same reasons photographers get very excited as resolutions on-camera increase, so should UAS photographers. Greater resolution doesn’t always mean higher grade images. Nor does larger sensor sizes increase quality of images. On the whole, higher resolution systems usually does translate into higher quality images.
Video cameras are acquisition devices. For the same reasons major motion pictures are acquired at the highest possible resolutions, and for the same reasons photographers get very excited as resolutions on-camera increase, so should UAS photographers. Greater resolution doesn’t always mean higher grade images. Nor does larger sensor sizes increase quality of images. On the whole, higher resolution systems usually does translate into higher quality images.
Sensor sizes are somewhat important to this discussion, yet not entirely critical. The camera industry has been packing more and more pixels into the same physical space for nearly two decades, without the feared increase in noise. Additionally, better noise-sampling/reduction algorithms, particularly from OEM’s like Sony and Ambarella, have allowed far greater reduction in noise compared to the past. Cameras such as the Sony A7RIV and earlier offer nearly noise-free ISO of 32,000!
Sensor sizes vary of course, but we’ll find most UAS utilize the 1/2.3, or the 1” sensor. (Light Blue and Turquoise sizes respectively, as seen below).
“Imagine an UAS equipped with an 8K camera inspecting a communications tower. Resolution is high, so small specs of rust, pitting, spalling, or other damage which might be missed with lower resolutions or the human eye become apparent with a greater resolution.”
WHY DOES HIGHER RESOLUTION TRANSLATE TO BETTER FINISHED PRODUCT?
Generally, we’re downsampling video or photos to smaller delivery vehicles, for but one reason. In broadcast, 4:2:2 uncompressed color schemes were the grail. Yet, most UAS cameras capture a 4:2:0 color/chroma sample. However, a 4K capture, downsampled to 1080 at delivery, offers videographers the same “grail” color schema of 4:2:2!
As we move into 6 or 8K, similar results occur. 8K downconverted to HD offers a 4:4:4 color sample.
CROPPING
We gain the ability to crop for post editing/delivery to recompose images without fear of losing resolution. This means that although the aircraft may shoot a wide shot, the image may be recomposed to a tighter image in post, so long as the delivery is smaller than the source/acquisition capture. For example, shooting 4K for 1080 delivery means that up to 75% of the image may be cropped without resolution loss.
As the image above demonstrates, it’s quite possible to edit 8K HEVC streams on a newer laptop. Performance is not optimal without a great deal of RAM and a good video card, as HEVC requires a fair amount of horsepower to decode. The greater point, is that we can edit images with deep recomposition. Moreover, we have more pixels to work with, providing greater color correction, color timing, and depth/saturation.
 For public safety, this is priceless. An 8K capture provides great ability to zoom/crop deeply into a scene and deliver much greater detail in HD or 4K delivery.
For public safety, this is priceless. An 8K capture provides great ability to zoom/crop deeply into a scene and deliver much greater detail in HD or 4K delivery.
The same can be said for inspections, construction progress reports, etc. Users can capture at a high resolution and deliver in a lower resolution.
Another benefit of 6 and 8K resolutions is the increase in dynamic range. While small sensors only provide a small increase in dynamic range, a small increase is preferable to no increase.
To address other statements about 6K and 8K resolutions; They human eye has the ability to see around 40megapixels, age-dependent. 8K is approximately 33megapixels. However, the human eye doesn’t see equal resolutions across the surface. The center of our eye sees approximately 8megapixels, where the outer edges are not as deep. High resolution does provide greater smoothing across the spectrum, therefore our eyes see smoother moving pictures.
BEYOND THE HUMAN EYE
Going well-beyond the human eye, higher resolutions are applicable to “computer vision,” benefiting mapping, 3D modeling, and other similar applications. Generally speaking, more pixels equals greater smoothness and geometry. As technology moves deeper into Artificial Intelligence, higher resolutions with more efficient codecs become yet even more important. Imagine an UAS equipped with an 8K camera inspecting a communications tower. Resolution is high, so small specs of rust or other damage which might be missed with lower resolutions or the human eye become more visible with a greater resolution. Now imagine that greater resolution providing input to an AI-aided inspection report that might notify the operator or manager of any problem. Our technology is moving beyond the resolution of the human eye for good reason.
DATA STORAGE
Files from a 6 or 8K camera are relatively small, particularly when compared to uncompressed 8K content (9.62TB per hour). Compression formats, known as “Codecs” have been improving for years, steadily moving forward. For example, when compressions first debuted in physical form, we saw Hollywood movies delivered on DVD. Then we saw HD delivered on Blu-ray. Delivery over disc formats is dead, and now we’ve moved through MPG2, AVC, AVCHD, H.264, and now H.265/HEVC. In the near future we’ll see yet even more compression schemes benefitting our workflows whether delivered via streaming or thumbdrive. VVC or “Versatile Video Codec”will be the next big thing in codecs for 8K, scheduled to launch early 2022.
Unconventional h.264 and H.265/HEVCare currently being used as delivery codecs for compressed 6 and 8K streams. 8K has been successfully broadcast (in testing environments) at rates as low as 35Mbps for VOD, while NHK has set the standard at 100Mbps for conventional delivery. Using these codecs, downconverting streams to view OTA/Over The Air to tablets, smartphones, or ground station controllers is already possible. It’s unlikely we’ll see 8K streaming from the UAS to the GSC.
U3 Datacards are certainly prepared for 6 and 8K resolutions/datastreams; compression is what makes this possible. The KenDao 8K and Insta 8K 360 cameras both are recording to U3 cards, available in the market today.
It will be some time before the average consumer will be seeing 8K on screens in their homes. However, 8K delivered for advertising, matching large format footage being shot on Weapon, Monstro, Helium or other camera formats may be less time-consuming when using 8K, even from smaller camera formats carried on an UAS (these cameras may easily be carried on heavy-lift UAS).
Professional UAS pilots will benefit greatly from 5, 6, or 8K cameras, and should not be shy about testing the format. Yes, it’s yet another paradigm shift in an always-fluid era of aerial and visual technology. There can be no doubt that these higher resolutions provide higher quality in any final product. Be prepared; 2020 is the year of 5, 6, and 8K cameras on the flying tripods we’re using for our professional and personal endeavors, and I for one, am looking forward to it with great enthusiasm.
 Douglas Spotted Eagle is the Founder and Director of Educational Programming at Sundance Media Group. SMG serves as a consultant within the sUAS industry, offering training and speaking engagements on sUAS topics: UAV cinematography, commercial and infrastructural sUAS applications, sUAS risk management, night UAV flight, aerial security systems, and 107 training. To learn more about codecs, compression/decompression, optimizing capture and data for streaming Ask about training and classes in “Cracking the Camera Code” seminars found online, in our training facility, or in your offices.
Douglas Spotted Eagle is the Founder and Director of Educational Programming at Sundance Media Group. SMG serves as a consultant within the sUAS industry, offering training and speaking engagements on sUAS topics: UAV cinematography, commercial and infrastructural sUAS applications, sUAS risk management, night UAV flight, aerial security systems, and 107 training. To learn more about codecs, compression/decompression, optimizing capture and data for streaming Ask about training and classes in “Cracking the Camera Code” seminars found online, in our training facility, or in your offices.







[…] Source link […]