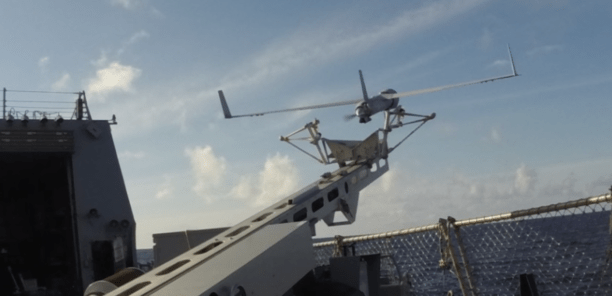
Ballard Power Systems has announced that a new high performance fuel cell propulsion system to power unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). In addition, they have received a follow-on contract from Boeing’s Insitu subsidiary for extended durability testing of the next-generation 1.3 kilowatt (kW) fuel cell propulsion system to power test flights of its ScanEagle UAV platform.
Ballard and Insitu have partnered over the past two years to integrate Ballard’s prior generation fuel cell propulsion system – a complete hydrogen power system for small unmanned fixed wing and Vertical Take Off and Landing (VTOL) platforms – into the ScanEagle platform. Successful flight testing was announced in mid-2017.
The next generation fuel cell propulsion system announced today delivers a number of important advances: increased power density, resulting from a new membrane electrode assembly (MEA) design; reduced cost, resulting from a combination of new MEA and one-step fuel cell stack sealing process; and extended lifetime. The increase in rated power, without any appreciable increase in size or weight, is a particularly significant development for UAV applications.
Phil Robinson, Vice President of Unmanned Systems at Protonex, a Ballard subsidiary, said, “The Ballard and Insitu teams have collaborated closely over the past several years to integrate our proven fuel cell technology into the industry-leading ScanEagle platform. This new fuel cell has the potential to deliver a range of benefits compared to the use of an internal combustion engine, or ICE, to power the ScanEagle. These benefits are likely to include an increase in reliability and available electrical power along with a simultaneous reduction in audible noise, thereby enabling lower altitude missions.”
Fuel cell propulsion systems offer a number of advantages over ICE-powered drones (refer to accompanying chart). In addition, fuel cells offer a 3x increase in mission time compared to battery-powered drones.
Andrew Duggan, Vice President and General Manager of Insitu Commercial added, “Insitu is pleased to continue our partnership with Ballard as we add capabilities, further increasing reliability and decreasing operating cost of the ScanEagle platform. We look forward to further performance tests and customer demonstrations in the coming year.”
ScanEagle is 1.55 meters (5.1 feet) in length, has a wingspan of 3.11 meters (10.2 feet) and maximum takeoff weight of 22 kilograms (48.5 lbs). The UAV can fly at a maximum speed of 41.2 meters per second (80 knots), reach a ceiling of 5,944 meters (19,500 feet). Additional details and images are available at http://www.insitu.com/
In addition to military use, the commercial market for drones is expected to growth significantly over the next few years, from 0.25 million working drones in 2017 to more than 2.5 million working drones by 2021.[1] Applications are anticipated in such areas as agriculture, construction, environmental management, urban & rural surveying, mining, emergency response and law enforcement.
You can learn more about Ballard’s work in the UAV area here.
Frank Schroth is editor in chief of DroneLife, the authoritative source for news and analysis on the drone industry: it’s people, products, trends, and events.
Email Frank
TWITTER:@fschroth




[…] 2017, Ballard released a new hydrogen fuel-cell propulsion system which led to a contract with Boeing’s Insitu subsidiary to power test flights of the company’s […]